monitoring endangered freshwater biodiversity using environmental dna
A Review Pritam Banerjee 1 2 Gobinda Dey 1 2 Caterina M. Including monitoring of endangered rare and invasive species.

Pdf Monitoring Endangered Freshwater Biodiversity Using Environmental Dna
Sources of eDNA can include shed skin cells feces hair and reproductive secretions.

. Uptake of eDNA methodologies into biomonitoring of invasive species for fisheries appears to be increasing with events such as the American Fisheries Society symposium in September 2013 entitled Environmental DNA eDNA Analysis a New Genetic Tool for Monitoring Managing and Conserving Fishery Resources and Aquatic Habitat which covered the topics of Asian carp in. In this review we summarize recent developments in eDNA technology and focus primarily on the operational procedure and its application for freshwater benthic macroinvertebrate. We further demonstrate that entire faunas of amphibians and fish can be detected by high-throughput sequencing of DNA extracted from pond water.
Reinforcement of Environmental DNA Based Methods Sensu Stricto in Biodiversity Monitoring and Conservation. We used conventional monitoring methods in parallel with environmental mitochondrial DNA-based species. Environmental DNA eDNA is a potentially powerful tool for detection and monitoring of rare species including threatened native species and recently arrived invasive species.
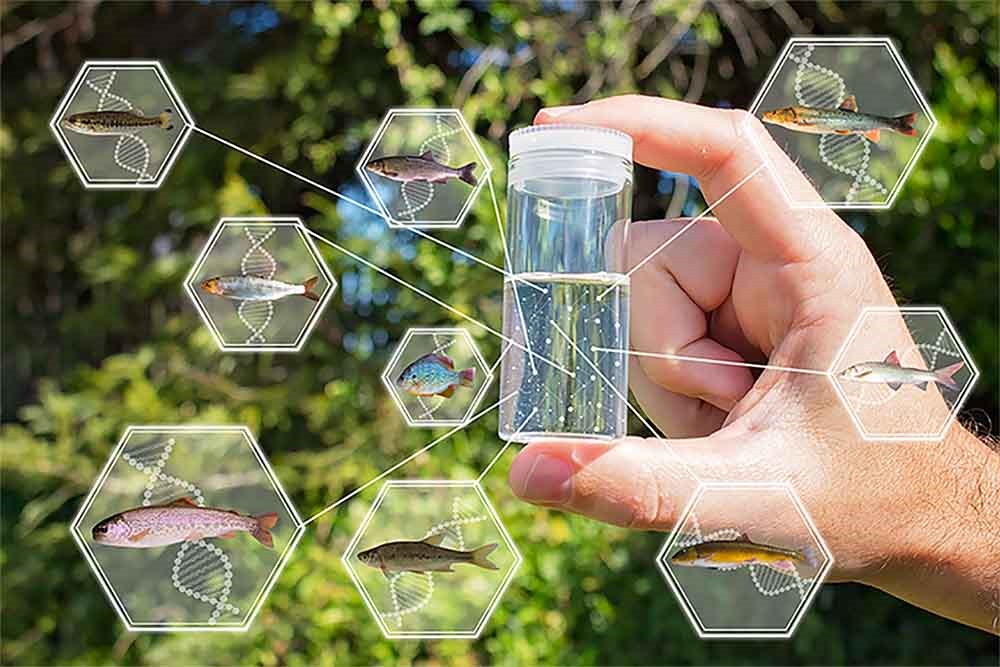
Our findings underpin the ubiquitous nature of DNA traces in the environment and establish environmental DNA as a tool for monitoring rare and threatened species across a wide range of taxonomic groups. Wildlife shed DNA into the environment thus becoming environmental DNA eDNA t. A proxy sity monitoring environmental DNA detection in wild for population density was calculated for the amphibi- populations has so far only been applied to a few com- ans Pelobates fuscus and Triturus cristatus using conven- mon or invasive species of amphibians and fish Ficet- tional monitoring based on active dip-netting and ola et al.
Using an eDNA-based method we estimated the presence of the invasive bluegill sunfish Lepomis macrochirus in 70 ponds located in seven locales on the Japanese mainland and on. Environmental DNA eDNA DNA fragments that are likely to be bound to organic matters in the water or in shed cells has been used to monitor the presence of aquatic animals. To address the potential of environmental DNA as a tool for monitoring rare and threatened freshwater spe-cies we conducted comparative surveys in natural lakes ponds streams and temporary pools in Europe.
Survey techniques using DNA collected from aquatic habitats may provide a cost-effective repeatable approach to sampling a large number of sites for many taxonomic groups Thomsen et al. Our findings underpin the ubiquitous nature of DNA traces in the environment and establish environmental DNA as a tool for monitoring rare and threatened species across a wide range of taxonomic groups. Environmental DNA eDNA metabarcoding is a relatively new monitoring tool featuring in an increasing number of applications such as the facilitation of the accurate and cost effective detection of species in environmental samples.
Previous studies have shown that diversity of rare and threatened European freshwater animals - representing amphibians fish mammals insects and crustaceans - can be detected and quantified based on environmental DNA eDNA obtained directly from small water samples of lakes ponds and streams Thomsen et al. Antognazza 3 Raju Kumar Sharma 2 4 Jyoti Prakash Maity 2 5 Michael W. Biodiversity monitoring of freshwater benthic macroinvertebrates using environmental DNA Li Meng 1.
The term environmental DNA refers to DNA that organisms shed into the environment. The objectives of this effort include improving long-term monitoring of fish and other aquatic species and early detection of aquatic invasive species. Environmental DNA eDNA monitoring enables the detection of organisms from DNA present and collected in water samples.
This eDNA is distributed throughout the landscape by rain wind or even other animals. PhD project - Monitoring freshwater fish communities using environmental DNA metabarcoding. Chan 1 Yi-Hsun Huang 2 Pin-Yun Lin 4 Hung-Chun Chao 2 Chung-Ming Lu 6 and Chien.
The process for measuring biodiversity within an ecosystem. EDNA monitoring is likely to have a major impact on the ability of salmonid aquaculture industry producers and their regulators to detect the. Here we develop DNA primers for a suite of nine sympatric freshwater turtles and use it to test whether turtle eDNA can be successfully detected in samples from aquaria and an.
Environmental DNA eDNA is a convenient biodiversity monitoring tool and many studies have focused on river and coastal areas while deepwater oceanic surveys are rare. EDNA samples are collected in the field. We further demonstrate that entire faunas of amphibians and fish can be detected by high-throughput sequencing of DNA extracted from pond water.
It is demonstrated that entire faunas of amphibians and fish can be detected by high-throughput sequencing of DNA extracted from pond water underpin the ubiquitous nature of DNA traces in the environment and establish environmental DNA as a tool for monitoring rare and threatened species across a wide range of taxonomic groups.

Pdf Monitoring Endangered Freshwater Biodiversity Using Environmental Dna

Sampling Areas For Environmental Dna Edna In The Amazon Forest A C Download Scientific Diagram

Proper Environmental Dna Metabarcoding Data Transformation Reveals Temporal Stability Of Fish Communities In A Dendritic River System Laporte 2021 Environmental Dna Wiley Online Library

Environmental Dna An Emerging Tool For Understanding Aquatic Biodiversity U S National Park Service
Pdf Monitoring Endangered Freshwater Biodiversity Using Environmental Dna

Pdf Monitoring Endangered Freshwater Biodiversity Using Environmental Dna
Environmental Dna For Biodiversity And Ecosystem Monitoring Molecular Ecology Vol 30 No 13

Fishing For Mammals Using Environmental Dna From Rivers To Monitor Mammals On Land The Applied Ecologist

Environmental Dna An Emerging Tool For Understanding Aquatic Biodiversity U S National Park Service

Diverse Applications Of Environmental Dna Methods In Parasitology Trends In Parasitology

3 Maps Help Explain Sao Paulo Brazil S Water Crisis Http Ow Ly Duraa Water Crisis Water Paulo
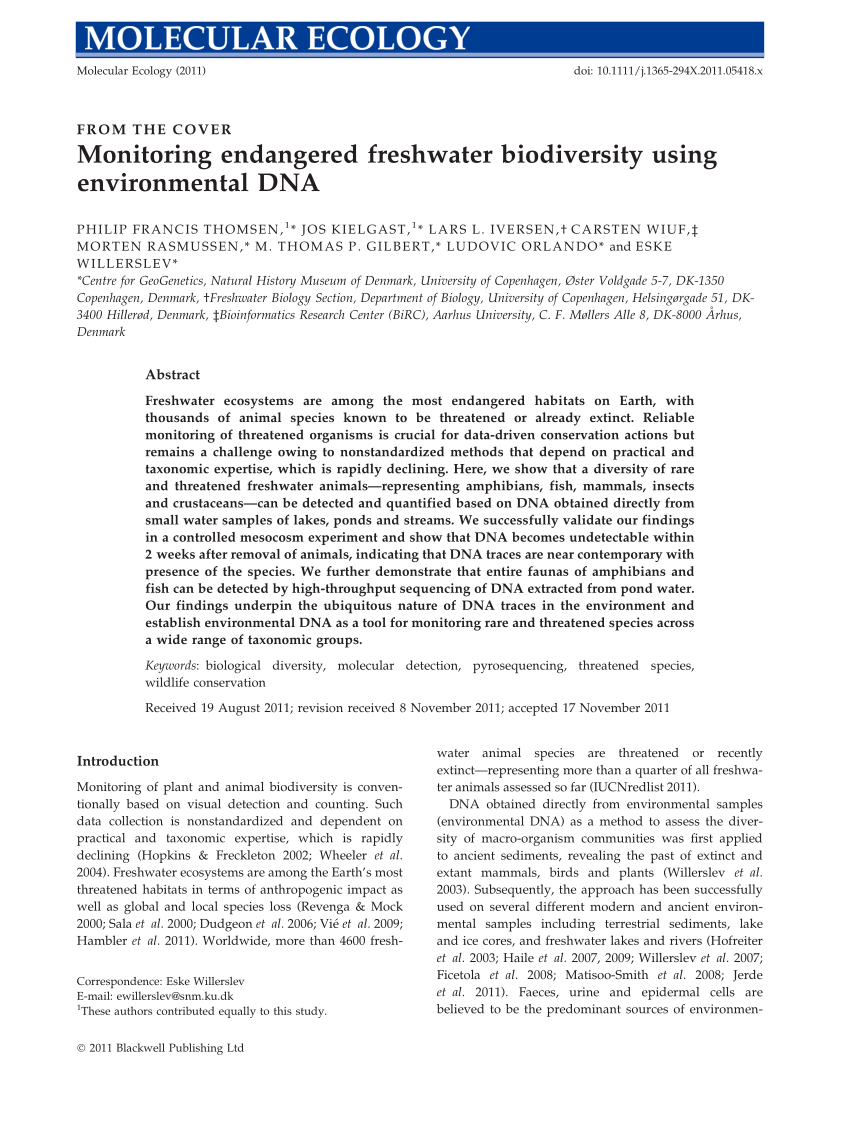
Frontiers Environmental Dna Monitoring Of Biodiversity Hotspots In Danish Marine Waters Marine Science

Environmental Dna For Wildlife Biology And Biodiversity Monitoring Trends In Ecology Evolution

Environmental Dna Metabarcoding For Benthic Monitoring A Review Of Sediment Sampling And Dna Extraction Methods Sciencedirect

Environmental Dna Helps Scientists Find Rare Aquatic Species
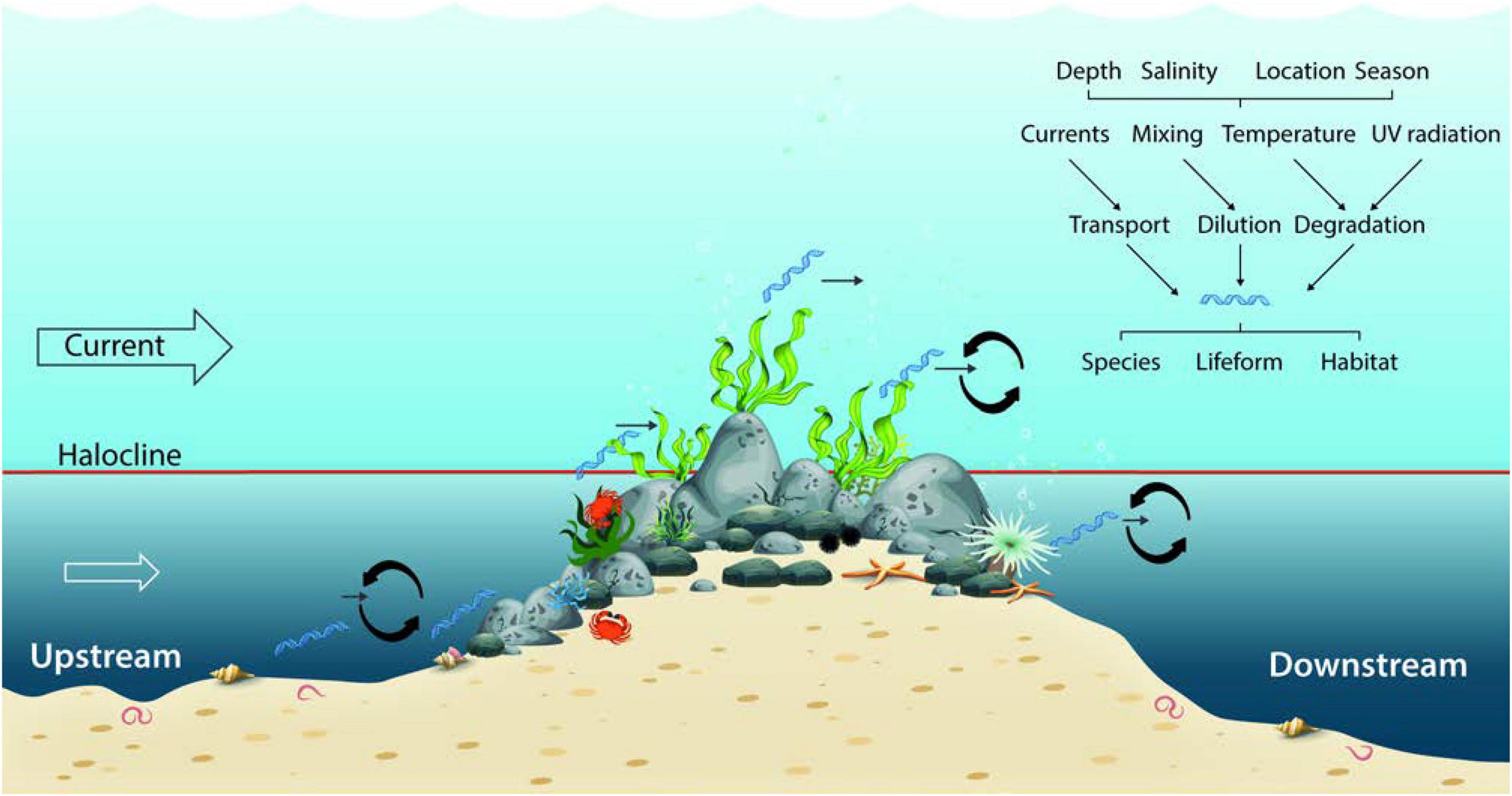
Frontiers A Model And Simulation Of The Influence Of Temperature And Amplicon Length On Environmental Dna Degradation Rates A Meta Analysis Approach Ecology And Evolution


Comments
Post a Comment